The Effects of Several Forms of Leaf Area Management and Different canopy heights with vertical shoot positioning on Berry Ripening and Wine Quality
Abstract
The goal of this research was to investigate different canopy heights and canopy management approaches in VSP-trained vineyards on the production of sugar and other substances present in berries and must, as well as on the resulting wine quality. Two sites, one high vigor and one low vigor, were selected for this study, with the following treatments tested: [1] ‘control’, shoots were topped according to standard practices; [2] ‘without lateral shoots’, all lateral shoots were removed; [3] ‘low canopy’, the canopy was shortened to 50 cm below the height of the ‘control’; [4] ‘twisted shoots’, shoots were not hedged, but instead were horizontally twisted along the upper wires. The ‘low canopy’ treatment revealed little effect on grape ripening parameters, especially in the low vigor trials. Upon sensory analysis, the quality of wine derived from this treatment did not score higher than the control, but rather repeatedly lower. Furthermore, ‘low canopy’ wines exhibited atypical aging notes, and in certain vintages more Berry shrivel was observed during the vegetative season. The ‘twisted shoots’ treatment displayed repeatedly higher YAN values in the must, especially in vineyards with higher vigor, which led to an increase in potential vine fertility. Thus, shortening the canopy was not found to be a suitable technique to delay ripening or improve wine quality.DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23796/LJ/2024.007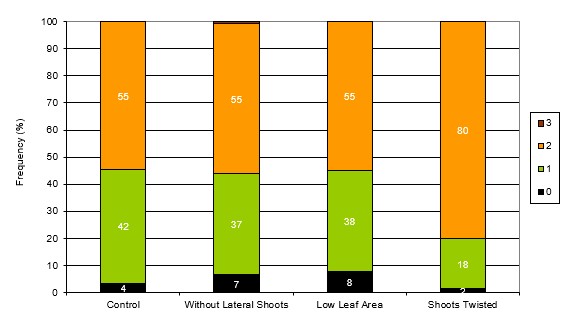
Downloads
Published
04.04.2024
How to Cite
Haas, F., Struffi, I., Pedri, U., & Sanoll, C. (2024). The Effects of Several Forms of Leaf Area Management and Different canopy heights with vertical shoot positioning on Berry Ripening and Wine Quality. Laimburg Journal, 6. https://doi.org/10.23796/LJ/2024.007
Issue
Section
Papers